算法一 knn 扩展 BBF算法,在KD-tree上找KNN ( K-nearest neighbor)
Step1: BBF算法,在KD-tree上找KNN。第一步做匹配咯~
1. 什么是KD-tree(from wiki)
K-Dimension tree,实际上是一棵平衡二叉树。
一般的KD-tree构造过程:
function kdtree (list of points pointList, int depth)
{
if pointList is empty
return nil;
else {
// Select axis based on depth so that axis cycles through all valid values
var int axis := depth mod k;
// Sort point list and choose median as pivot element
select median by axis from pointList;
// Create node and construct subtrees
var tree_node node;
node.location := median;
node.leftChild := kdtree(points in pointList before median, depth+1);
node.rightChild := kdtree(points in pointList after median, depth+1);
return node;
}
}
【例】pointList = [(2,3), (5,4), (9,6), (4,7), (8,1), (7,2)] tree = kdtree(pointList)
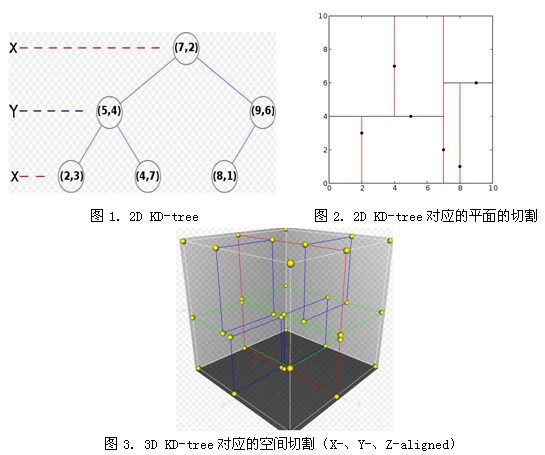
2. BBF算法,在KD-tree上找KNN ( K-nearest neighbor)
BBF(Best Bin First)算法,借助优先队列(这里用最小堆)实现。从根开始,在KD-tree上找路子的时候,错过的点先塞到优先队列里,自己先一个劲儿扫到leaf;然后再从队列里取出目前key值最小的(这里是是ki维上的距离最小者),重复上述过程,一个劲儿扫到leaf;直到队列找空了,或者已经重复了200遍了停止。
Step1: 将img2的features建KD-tree; kd_root = kdtree_build( feat2, n2 );。在这里,ki是选取均方差最大的那个维度,kv是各特征点在那个维度上的median值,features是你率领的整个儿子孙子特征大军,n是你儿子孙子个数。
|
/** a node in a k-d tree */ struct kd_node{ int ki; /**< partition key index */ double kv; /**< partition key value */ int leaf; /**< 1 if node is a leaf, 0 otherwise */ struct feature* features; /**< features at this node */ int n; /**< number of features */ struct kd_node* kd_left; /**< left child */ struct kd_node* kd_right; /**< right child */ }; |
Step2: 将img1的每个feat到KD-tree里找k个最近邻,这里k=2。
k = kdtree_bbf_knn( kd_root, feat, 2, &nbrs, KDTREE_BBF_MAX_NN_CHKS );
|
min_pq = minpq_init(); minpq_insert( min_pq, kd_root, 0 ); while( min_pq->n > 0 && t < max_nn_chks ) //队列里有东西就继续搜,同时控制在t<200(即200步内) { expl = (struct kd_node*)minpq_extract_min( min_pq ); //取出最小的,front & pop expl = explore_to_leaf( expl, feat, min_pq ); //从该点开始,explore到leaf,路过的“有意义的点”就塞到最小队列min_pq中。 for( i = 0; i < expl->n; i++ ) // { tree_feat = &expl->features[i]; bbf_data->old_data = tree_feat->feature_data; bbf_data->d = descr_dist_sq(feat, tree_feat); //两feat均方差 tree_feat->feature_data = bbf_data; n += insert_into_nbr_array( tree_feat, _nbrs, n, k ); //按从小到大塞到neighbor数组里,到时候取前k个就是 KNN 咯~ n 每次加1或0,表示目前已有的元素个数 } t++; } |
对“有意义的点”的解释:
|
struct kd_node* explore_to_leaf( struct kd_node* kd_node, struct feature* feat, struct min_pq* min_pq )//expl, feat, min_pq { struct kd_node* unexpl, * expl = kd_node; double kv; int ki; while( expl && ! expl->leaf ) { ki = expl->ki; kv = expl->kv; if( feat->descr[ki] <= kv ) { unexpl = expl->kd_right; expl = expl->kd_left; //走左边,右边点将被记下来 } else { unexpl = expl->kd_left; expl = expl->kd_right; //走右边,左边点将被记下来 } minpq_insert( min_pq, unexpl, ABS( kv - feat->descr[ki] ) ) ;//将这些点插入进来,key键值为|kv - feat->descr[ki]| 即第ki维上的差值 } return expl; } |
Step3: 如果k近邻找到了(k=2),那么判断是否能作为有效特征,d0/d1<0.49就算是咯~
|
d0 = descr_dist_sq( feat, nbrs[0] );//计算两特征间squared Euclidian distance d1 = descr_dist_sq( feat, nbrs[1] ); if( d0 < d1 * NN_SQ_DIST_RATIO_THR )//如果d0/d1小于阈值0.49 { pt1 = cvPoint( cvRound( feat->x ), cvRound( feat->y ) ); pt2 = cvPoint( cvRound( nbrs[0]->x ), cvRound( nbrs[0]->y ) ); pt2.y += img1->height; cvLine( stacked, pt1, pt2, CV_RGB(255,0,255), 1, 8, 0 );//画线 m++;//matches个数 feat1[i].fwd_match = nbrs[0]; } |
Step2: 通过RANSAC算法来消除错配,什么是RANSAC先?
1. RANSAC (Random Sample Consensus, 随机抽样一致) (from wiki)
该算法做什么呢?呵呵,用一堆数据去搞定一个待定模型,这里所谓的搞定就是一反复测试、迭代的过程,找出一个error最小的模型及其对应的同盟军(consensus set)。用在我们的SIFT特征匹配里,就是说找一个变换矩阵出来,使得尽量多的特征点间都符合这个变换关系。
算法思想:
input:
data - a set of observations
model - a model that can be fitted to data
n - the minimum number of data required to fit the model
k - the maximum number of iterations allowed in the algorithm
t - a threshold value for determining when a datum fits a model
d - the number of close data values required to assert that a model fits well to data
output:
best_model - model parameters which best fit the data (or nil if no good model is found)
best_consensus_set - data point from which this model has been estimated
best_error - the error of this model relative to the data
iterations := 0
best_model := nil
best_consensus_set := nil
best_error := infinity
while iterations < k //进行K次迭代
maybe_inliers := n randomly selected values from data
maybe_model := model parameters fitted to maybe_inliers
consensus_set := maybe_inliers
for every point in data not in maybe_inliers
if point fits maybe_model with an error smaller than t //错误小于阈值t
add point to consensus_set //成为同盟,加入consensus set
if the number of elements in consensus_set is > d //同盟军已经大于d个人,够了
(this implies that we may have found a good model,
now test how good it is)
better_model := model parameters fitted to all points in consensus_set
this_error := a measure of how well better_model fits these points
if this_error < best_error
(we have found a model which is better than any of the previous ones,
keep it until a better one is found)
best_model := better_model
best_consensus_set := consensus_set
best_error := this_error
increment iterations
return best_model, best_consensus_set, best_error
2. RANSAC去除错配:
H = ransac_xform( feat1, n1, FEATURE_FWD_MATCH, lsq_homog, 4, 0.01,homog_xfer_err, 3.0, NULL, NULL );
|
nm = get_matched_features( features, n, mtype, &matched ); /* initialize random number generator */ rng = gsl_rng_alloc( gsl_rng_mt19937 ); gsl_rng_set( rng, time(NULL) ); in_min = calc_min_inliers( nm, m, RANSAC_PROB_BAD_SUPP, p_badxform ); //符合这一要求的内点至少得有多少个 p = pow( 1.0 - pow( in_frac, m ), k ); i = 0; while( p > p_badxform )//p>0.01 { sample = draw_ransac_sample( matched, nm, m, rng ); extract_corresp_pts( sample, m, mtype, &pts, &mpts ); M = xform_fn( pts, mpts, m ); if( ! M ) goto iteration_end; in = find_consensus( matched, nm, mtype, M, err_fn, err_tol, &consensus); if( in > in_max ) { if( consensus_max ) free( consensus_max ); consensus_max = consensus; in_max = in; in_frac = (double)in_max / nm; } else free( consensus ); cvReleaseMat( &M ); iteration_end: release_mem( pts, mpts, sample ); p = pow( 1.0 - pow( in_frac, m ), ++k ); } /* calculate final transform based on best consensus set */ if( in_max >= in_min ) { extract_corresp_pts( consensus_max, in_max, mtype, &pts, &mpts ); M = xform_fn( pts, mpts, in_max ); in = find_consensus( matched, nm, mtype, M, err_fn, err_tol, &consensus); cvReleaseMat( &M ); release_mem( pts, mpts, consensus_max ); extract_corresp_pts( consensus, in, mtype, &pts, &mpts ); M = xform_fn( pts, mpts, in ); |
思考中的一些问题:
features间的对应关系,记录在features->fwd_match里(matching feature from forward
imge)。
1. 数据是nm个特征点间的对应关系,由它们产生一个3*3变换矩阵(xform_fn = hsq_homog函数,此要>=4对的对应才可能计算出来咯~),此乃模型model。
2. 然后开始找同盟军(find_consensus函数),判断除了sample的其它对应关系是否满足这个模型(err_fn = homog_xfer_err函数,<=err_tol就OK~),满足则留下。
3. 一旦大于当前的in_max,那么该模型就升级为目前最牛的模型。(最最原始的RANSAC是按错误率最小走的,我们这会儿已经保证了错误率在err_tol范围内,按符合要求的对应数最大走,尽量多的特征能匹配地上)
4. 重复以上3步,直到(1-wm)k <=p_badxform (即0.01),模型就算找定~
5. 最后再把模型和同盟军定一下,齐活儿~
声明:以上代码参考Rob Hess的SIFT实现。
算法一 knn 扩展 BBF算法,在KD-tree上找KNN ( K-nearest neighbor)相关推荐
- K NEAREST NEIGHBOR 算法(knn)
K Nearest Neighbor算法又叫KNN算法,这个算法是机器学习里面一个比较经典的算法, 总体来说KNN算法是相对比较容易理解的算法.其中的K表示最接近自己的K个数据样本.KNN算法和K-M ...
- K Nearest Neighbor 算法
K Nearest Neighbor算法又叫KNN算法,这个算法是机器学习里面一个比较经典的算法, 总体来说KNN算法是相对比较容易理解的算法.其中的K表示最接近自己的K个数据样本.KNN算法和K-M ...
- 机器学习之深入理解K最近邻分类算法(K Nearest Neighbor)
[机器学习]<机器学习实战>读书笔记及代码:第2章 - k-近邻算法 1.初识 K最近邻分类算法(K Nearest Neighbor)是著名的模式识别统计学方法,在机器学习分类算法中占有 ...
- kd tree python_Python实现KNN与KDTree
KNN算法: KNN的基本思想以及数据预处理等步骤就不介绍了,网上挑了两个写的比较完整有源码的博客. 利用KNN约会分类 KNN项目实战--改进约会网站的配对效果 KNN 代码 ''' Functio ...
- 机器学习——K近邻算法(KNN)(K Nearest Neighbor)
参考视频与文献: python与人工智能-KNN算法实现_哔哩哔哩_bilibili 机器学习--K近邻算法(KNN)及其python实现_清泉_流响的博客-CSDN博客_python实现knn 机器 ...
- kNN算法(k近邻算法,k Nearest Neighbor)
主要内容: 1.认识kNN算法 2.kNN算法原理 3.应用举例 4.kNN改进方法 1.认识knn算法 "看一个人怎么样,看他身边的朋友什么样就知道了",kNN算法即寻找最近的K ...
- 机器学习降维算法一:PCA(主成分分析算法)
引言: 机器学习领域中所谓的降维就是指采用某种映射方法,将原高维空间中的数据点映射到低维度的空间中.降维的本质是学习一个映射函数 f : x->y,其中x是原始数据点的表达,目前最多使用向量表达 ...
- 特征匹配-NNDR策略,kd树,BBF算法
特征匹配需要考虑匹配策略和如何更快的完成匹配. 一:以欧式距离为度量,有三种匹配策略:固定阈值.最近邻.最近邻距离比率(NNDR) 固定阈值:就是设定一个阈值,当距离大于阈值,判为不匹配,否则判为匹配 ...
- k-d tree算法原理及实现
k-d tree即k-dimensional tree,常用来作空间划分及近邻搜索,是二叉空间划分树的一个特例.通常,对于维度为k,数据点数为N的数据集,k-d tree适用于N≫2k的情形. 1)k ...
最新文章
- 【错误记录】SeeMusic 一直卡在主界面无法使用 ( 删除 C:\Users\用户名称\AppData\LocalLow\Visual Music Design 应用信息 )
- Dubbo管控台Windows安装
- 详解DPoS共识算法
- HFSS安装提示failed to check out license during initialization,怎么解决?
- UVA - 1533Moving Pegs移动小球 (bfs加状态压缩)
- VREP中的力触觉设备接口(CHAI3D)
- 部署gogs_可以更快地查阅 Gogs 文档了!
- delphi chart 曲线实时_发展学生曲线跑能力的体育游戏及运用研究
- HTML5---新标签与特性
- Arcgis 连接PostgreSQL
- 用计算机显示器主屏区域造句,显示器造句
- 瞬态二极管,有哪些?
- 使用Eclipse编译运行MapReduce程序_Hadoop2.6.0_Ubuntu/CentOS
- Linux常用命令--软件包管理之(服务管理)
- 13.2-“制作一款私有IAP串口下载小工具”之串口IAP的通信协议设计
- Java小游戏实操---大鱼吃小鱼 游戏开发
- Python3 获取法定节假日
- 给小白的论文写作方法!实用率99%!
- CNN中十大拍案叫绝的操作
- 软件测试(开发)工程师的核心竞争力是什么?
