python图像_Python图像处理库(PIL)
Python Imaging Library为您的python程序添加图像处理能力。这个库提供广泛的文件格式支持、高效的内部表示和相当强大的图像处理能力。
核心图像库是为快速访问几种基本像素格式图像设计的。它能为一般的图像处理工具提供一个可靠的基础。
这个Pythonic library可以
装载和保存多种格式文件 Loading and Saving images (diverse formats)
Python Imaging Library的最新版本可以识别并读取多数图像格式。写图像操作则有意地限制为最常用的交流和发布的格式。 convert images between different pixel representations 图像格式转换
缩放、裁剪、合成、变换和通道 Scaling, cropping, compositing, transforms, bands (the separate color channels e.g. alpha channel 半透明通道)
The library also supports image resizing, rotation and arbitrary affine transforms.提供图像缩放,旋转和任意仿射变换的支持。
图像增强 Image Enhancementpoint operations,filtering with a set of built-in convolution kernels, and colour space conversions. 像素操作,内置convolution kernel的滤镜和颜色空间变换
adjust contrast, brightness, colour balance and sharpness using the ImageEnhance module
直方图、对比增强和统计分析 histogram,contrast enhancement,statistical analysis
There‘s a histogram method allowing you to pull some statistics out of an image. This can be used for automatic contrast enhancement, and for global statistical analysis.提供histogram方法使您可以输出对某个图像的一些统计信息。这可以用于自动对比增强和全局统计分析。
绘制文字和基本图形 Drawing text and basic shapes
图像序列(动画) Image Sequences
Supported sequence formats include FLI/FLC, GIF, and a few experimental formats. TIFF files can also contain more than one frame.
图像显示 Image DisplayThe current release includes Tk PhotoImage and BitmapImage interfaces, as well as a Windows DIB interface that can be used with PythonWin. For X and Mac displays, you can use Jack Jansen‘s img library.最新发布版本包含Tk PhotoImage and BitmapImage 接口,Windows DIB 接口也可以随着PythonWin一起使用。而对了X 和Mac系统的显示,您可以使用Jack Jansen的图像库。
For debugging, there‘s also a showmethod in the Unix version which calls xv to display the image. Debug版本中,于Unix也提供show方法调用xv来显示图像
图像打印 Postscript Printingprint images, text and graphics on Postscript printers
几个应用的例子:
图像大小及格式转换 Image resizing or format conversions
添加保存/装载功能到程序 Adding save/load support into your application
图表 Chart generation (also see PIDDLE piddle.sf.net)
生成缩略图 Thumbnail generation
水印和图例 Watermarking or adding legend
基本概念 PIL API - Concepts
尺寸Sizes
The size attribute is a 2-tuple containing width and height (in pixels).
通过图片对象的size属性可以得到图片的尺寸,结果这是一个二元组,包含水平和垂直方向上的像素数。
坐标Coordinates
The graphics interface uses the same coordinate system as PIL itself, with (0, 0) in the upper left corner.
Pil采取左上角为(0,0)的坐标系统
角度 AnglesAngles are given in degrees. Zero degrees is in the +x (east) direction, and the angle increases
counter-clockwise,in the usual Cartesian convention. For example, angle 45 points northeast.
边界框 Bboxes(Bounding boxes)
A bounding box or bbox is a rectangle(矩形) in the image. It is defined by a 4-tuple, (x0, y0, x1, y1) where (x0,y0) is the top left (northwest) corner of the rectangle, and (x1, y1) is the bottom right (southeast) corner.
Generally, the area described by a bounding box will include point (x0, y0), but it will not include point (x1, y1) or the row and column of pixels containing point (x1, y1).
For example, drawing an ellipse inside the bounding box (0,0,5,10) will produce an ellipse 5 pixels
wide and 10 pixels high. The resulting ellipse will include pixel column 4 but not column 5, and will
also include pixel row 9 but not row 10.
由四元组(x0, y0, x1, y1)定义的一个矩形区域。区域包括左上角(x0,y0),但不包括右下角(x1, y1)或者(x1, y1)所在行列的像素点。
通道 Bands – the separate color channels
An image band is a set of values, one per image pixel.
Monochrome(黑白) or grayscale images have one band;color images in the RGB system have three bands, CMYK images have four, and so on.
Photoshop users will recognize bands as similar to Photoshop channels.
一个图片可以包含一到多个数据通道,如果这些通道具有相同的维数和深度,Pil允许将这些通道进行叠加.
在RGB模式下,每个图片由三个通道叠加而成,每个模式下为一个灰度图,当有一个调色板来调色的时候,这三张灰度图的叠加即可合成3*8位(每个像素)的一个真彩图片。
pil库中,图片之间的模式(mode)可以转化。
>>> bands = im.split ()
>>> rIm = bands [0]
>>> aIm = bands [3]
>>> remadeImage = Image.merge (“RGBA”, (rIm, gIm, bIm, aIm))
>>> grayscaleIm = Image.open (“myAlpha.gif”)
>>> remadeImage = myImage.putalpha (grayscaleIm) # replace the alpha band
模式 Mode
the number and names of the bands in the image, and also the pixel type and depth.
Common modes are "L" (luminance) for greyscale images, "RGB" for true colour images, and "CMYK" for pre-press images.
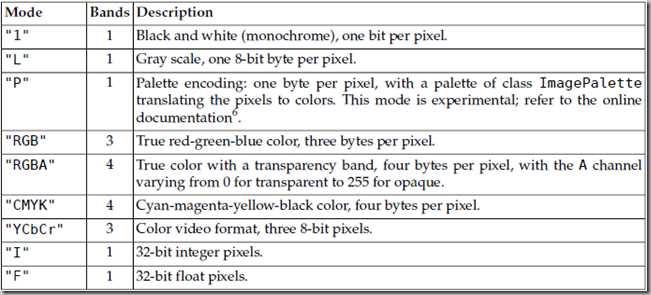
1 (1-bit pixels, black and white, stored with one pixel per byte)
1位像素,黑和白,存成8位的像素
L (8-bit pixels, black and white)
8位像素,黑白
P (8-bit pixels, mapped to any other mode using a colour palette)
8位像素,使用调色板映射到任何其他模式
RGB (3x8-bit pixels, true colour)
3×8位像素,真彩
RGBA (4x8-bit pixels, true colour with transparency mask)
4×8位像素,真彩+透明通道
CMYK (4x8-bit pixels, colour separation)
4×8位像素,颜色隔离
YCbCr (3x8-bit pixels, colour video format)
3×8位像素,彩色视频格式
I (32-bit integer pixels)
32位整型像素
F (32-bit floating point pixels)
32位浮点型像素
调色板 Palette
mode("P")为每个像素定义具体的颜色值
颜色 Color – 32位数值、元组或字符串 specified as 32bit value, tuple, or string
单通道图像-像素数值32bit value
For single-band images, the color is the pixel value.
For “1”, “L”, and “I” images, use integers.
For “F” images, use integer or floating point values.
For palette images (mode “P”), use integers as colour indexes.
For example, in a mode "1" image, the color is a single integer, 0 for black, 1 for white.
For mode "L", it is an integer in the range [0,255], where 0 means black and 255 means white.
多通道图像-像素元组tuple
For multi-band images, supply a tuple with one value per band.
For “RGB” images, use a 3-tuple containing integer values.The tuple (255,0,0) is pure red.
字符串常量 In 1.1.4 and later, you can also use RGB 3-tuples or colour names (see below). 颜色对照表
CSS风格的颜色字符串
Hexadecimal color specifiers, given as “#rgb” or “#rrggbb”. For example, “#ff0000”specifies pure red.
RGB像素值
RGB functions, given as “rgb(red, green, blue)” where the colour values are integers in the range 0 to 255. Alternatively, the color values can be given as three percentages (0% to 100%). For example, “rgb(255,0,0)” and “rgb(100%,0%,0%)” both specify pure red.
HSL色彩模式
Hue-Saturation-Lightness (HSL) functions, given as “hsl(hue, saturation%, lightness%)”
hue is the colour given as an angle between 0 and 360 (red=0, green=120, blue=240),
saturation is a value between 0% and 100% (gray=0%, full color=100%
lightness is a value between 0% and 100% (black=0%, normal=50%, white=100%).
For example, “hsl(0,100%,50%)” is pure red.
通过对色调(H)、饱和度(S)、亮度(L)三个颜色通道的变化以及它们相互之间的叠加来得到各式各样的颜色。
常见HTML颜色名称
Common HTML colour names. The ImageDraw provides some 140 standard colour names, based on the colors supported by the X Window system and most web browsers. Colour names are case insensitive, and may contain whitespace.
For example, “red” and “Red” both specify pure red.
滤镜 Resampling Filters
Some operations that reduce the number of pixels, such as creating a thumbnail, can use different filters to compute the new pixel values. These include:
在对图片的几何操作中可能会将多个输入像素映射到单个的输出像素(减少像素量,比如说创建缩略图),可以使用不同滤镜来计算新的像素。pil提供4种不同的采样滤镜(在目前的版本中,后续的版本可能支持更多):
1 NEAREST最近
Uses the value of the nearest pixel.
2 BILINEAR双线性
Uses linear interpolation over a 2x2 set of adjacent pixels.
3 BICUBIC双三次
Uses cubic interpolation over a 4x4 set of pixels.
4 ANTIALIAS平滑
Neighboring pixels are resampled to find the new pixel value.
例如,Image对象有三种使用filter的方法
1 resize(size,filter=None)
返回指定大小的一个新图像对象,可以使用一个filter参数来指明内插方式,默认采用NEAREST
>>> smallIm = im.resize ( (128, 128), Image.ANTIALIAS)
2 thumbnail(size,filter=None)
有两个特点:
1 改变原图 Modifies in-place
2 保持比例 aspect ratio(height : width)) -- size为(400,150)的im, im.thumbnail((40,40))后变为(40,15)3 filter(name)
Return a copy of the image filtered through a named image enhancement filter.
有专门的ImageFilter模块来支持Image enhancement。
字体 Fonts
PIL可以使用bitmap fonts或者OpenType/TrueType fonts.
Bitmap fonts are stored in PIL’s own format, where each font typically consists of a two files, one named .pil and the other usually named .pbm. The former contains font metrics, the latter raster data.
To load a bitmap font, use the load functions in the ImageFont module.
To load a OpenType/TrueType font, use the truetype function in the ImageFont module. Note that this function depends on third-party libraries, and may not available in all PIL builds.(IronPIL)
To load a built-in font, use the Font constructor in the ImageFont module.
有专门的ImageFont模块来支持ImageDraw模块中.text()方法中的字体选项。
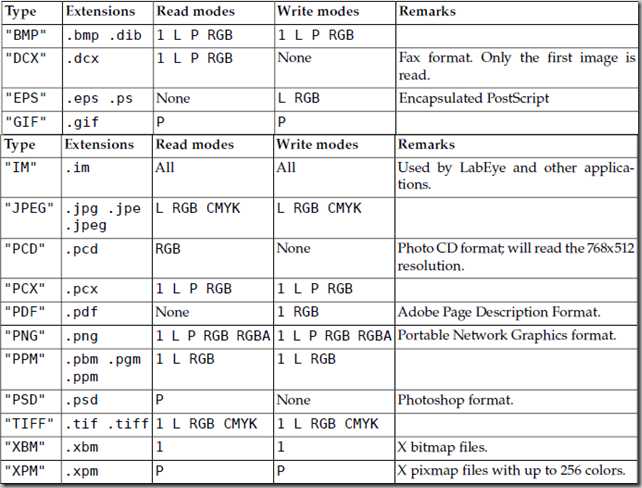
文件格式 Format
The format attribute identifies the source of an image. If the image was not read from a
file, it is set to None.
文件类型码(Type列)出现在Image.format属性和Image.save()方法中:
>>> im.save (“vacation.png”) #OR
>>> im.save (“vacation.png”, "PNG”)
常用操作
合成 Image.blend(i1,i2,a)/Image.composite(i1,i2,mask)
缩略图 thumbnail(size,filter=None)Modifies in-place,Preserves aspect ratio
>>> myImage.thumbnail ((128, 128), Image.ANTIALIAS)
剪切 crop(bbox)
>>> bounds = (100, 100, 400, 400)
>>> cutoutIm = myImage.crop (bounds)
粘贴 paste(i2,where,mask=None)/paste(color,box=None,mask=None)
旋转 rotate(theta)rotated around its center
翻转旋转 transpose(method)ROTATE_90/180/270(clockwise), FLIP_TOP_BOTTOM(horizontal), FLIP_RIGHT_LEFT(vertical)
>>> fixedIm = myImage.transpose (ROTATE_90)
The Image Module
The Image module provides
a class with the same name which is used to represent a PIL image.
The module also provides a number of factory functions(including functions to load images from files, and to create new images)
图像对象 Image – from file or newly created
所有的图片操作必须有一个操作对象,例如Pil提供open(filename)进行这个过程,此后,一切关于图片的操作均基于这个对象。有以下几种创建image对象的方式:
1 Image.open(f)
>>> import Image
>>>
>>> Im = Image.open("lena.jpg")
>>> print Im.mode,Im.size,Im.format
RGB (256, 256) JPEG
>>> Im.show()

如果文件不能打开,会抛出IOError异常。
可以查看image对象的format,mode,size,palette,info几个属性。
调用im.show()会在图片查看工具中显示当前操作的image对象。
标准版本的show方法的实现不太高效,因为它先把image保存到一个临时文件,然后调用xy工具来显示图像。如果你没有安装xy,那么它就无法工作了。不过如果它可以工作,倒还是非常方便用来debug和测试。
2 Image.new(mode,size,color=None)
color的默认值是黑色,这里我们新建一个红色的图像。
>>> newIm = Image.new (“RGBA”, (640, 480), (255, 0, 0)) #新建一个image对象creating images from scratch
3 Image.blend(i1,i2,a) -- (p1 x (1 - a) + p2 x a)
选一张灰度图(L)做背景,和雷娜图(RGB)做blend操作

>>> Im2 = Image.open("background.jpg").convert(Im.mode)
>>> Im2 = Im2.resize(Im.size)
>>> Im2.show()
>>>
>>> img = Image.blend(Im,Im2,0.2)
>>> img.show()

操作完毕后save(filename)用以保存这个临时的image对象img到硬盘。
4 Image.composite(i1,i2,mask) --equal-sized images i1 ,i2 and mask("1", "L", or "RGBA") (p1 x (1 - m) + p2 x m)
5 Image.eval(f,i) -- applying a function f to each pixel of image i
6 Image.merge(mode,bandList) --Creates a multi-band image from a sequence of single-band images of equal size
以下是Image对象的全部方法:
save(f,format=None)
保存
如果f是一个file对象,必须指定format(format codes)
convert(mode)
转换mode
copy()
crop(bbox)
剪切
原图中bbox区域
filter(name)
滤镜
the name of predefined image enhancement filters
滤镜名字需要import ImageFilter
getbands()
通道的字符串序列
如RGB图返回(‘R‘, ‘G‘, ‘B‘)
getbbox()
包含非零区域的最小bbox
getextrema()
最大最小像素点值
min&max pixel value
单通道图:返回元组(min,max)
多通道图:返回各个通道的元组组成的元组
getpixel(xy)
取像素点值
坐标xy处的pixel value or a sequence of pixel values
histogram(mask=None)
统计直方图
单通道图:返回列表[c0, c1, ...],ci是值为i的像素数
多通道图:a single sequence that is the concatenation of the sequences for all bands
mask参数:a same-sized mask image of mode "1" or "L"(include only those pixels correspond to nonzero pixels in the mask argument)
offset(dx,dy=None)
平移
Returns a new image the same size as the original, but with all pixels rotated dx in the +x direction,and dy in the +y direction.
If dy is omitted, it defaults to the same value as dx.
paste(i2,where,mask=None)
粘贴图片
where参数可以是
1 (x,y)坐标对:i2的像素点(0,0)对齐原图中的(x,y)粘贴,i2超过原图边界的部分被抛弃
2 bbox:i2必须和该bounding box大小一致
3 None:i2必须和原图大小一致
如果i2的mode和原图不一致,粘贴前会被转换。
mask参数:a same-sized mask image of mode "1","L" or “RGBA ”(control which pixels get replaced)
paste(color,box=None,mask=None)
填充颜色
如果box省略,整个图被填充为color色;mask参数同上
point(function)
改变像素点(函数)
Returns a new image with each pixel modified.
point(table)
改变像素点(查表)
To translate pixels using a table(a sequence of 256n values, where n is the number of bands in the image) lookup
putalpha(band)
改变alpha通道
The pixels of the band image(same-sized,"L" or "1") replace the alpha band(A) of the original image(RGBA) in place.
putpixel(xy, color)
改变单个像素点颜色
Note that this method is relatively slow. For more extensive changes, use paste or the ImageDraw module instead.
resize(size,filter=None)
调整大小
rotate(theta)
旋转(围绕图片中心)
Any pixels that are not covered by rotation of the original image are set to black.
show()
显示图片
On Unix systems, this method runs the xv image viewer to display the image.
On Windows boxes,the image is saved in BMP format and can be viewed using Paint.
This can be useful for debugging.
split()
分离通道
返回各个通道的灰度图组成的元组
Returns a tuple containing each band of the original image as an image of mode "L".
For example, applying this method to an "RGB" image produces a tuple of three images, one each for the red, green, and blue bands.
thumbnail(size,filter=None)
缩略图
Modifies in-place,Preserves aspect ratio
transform(xs, ys, Image.EXTENT, (x0,y0,x1,y1))
Returns a transformed copy of the image. In the transformed image, the point originally at (x0,y0) will appear at (0,0), and point (x1,y1) will appear at (xs, ys).
transform(xs, ys, Image.AFFINE, (a,b,c,d,e,f))
affine变换
The values a through f are the first two rows of an affine transform matrix.
Each pixel at (x,y) in the resulting image comes from position (ax+by+c,dx+ey+f) in the input
image, rounded to the nearest pixel.
transpose(method)
翻转旋转
ROTATE_90/180/270(clockwise), FLIP_TOP_BOTTOM(horizontal), FLIP_RIGHT_LEFT(vertical)
The ImageDraw Module
支持2D图像 The ImageDraw module provide basic 2D graphics support for Image objects.
It can for example be used to
create new images,
annotate or retouch existing images, and to generate graphics on the fly for web use.
For a more advanced drawing library for PIL, see The aggdraw Module.
创建绘画对象 ImageDraw module creates drawing surface for image
import Image, ImageDraw
im = Image.open(“vacation.jpeg")
drawSurface = ImageDraw.Draw(im)
基本绘画操作 Basic methods of drawing surface
弧/弦/扇形 chord arc pieslice (bbox, strtAng, endAng)
椭圆 ellipse (bbox)
线段/多段线 line (L) draw.line(((60,60),(90,60), (90,90), (60,90), (60,60))) #draw a square
点 point (xy) #单像素点很小看不清,实际中可用实心小圆代替
多边形 polygon (L) draw.polygon([(60,60), (90,60), (90,90), (60,90)]) #draw a square
矩形 rectangle (bbox) # first coord属于矩形, second coord不属于
文字 text(xy,message,font=None) 绘制文字message,文本区域左上角坐标为xy
drawable.text((10, 10), "Hello", fill=(255,0,0), font=None)
文字大小 textsize(message,font=None) 给定文字message,返回所占像素(width,height)
可选参数 Common optional args for these methods
fill=fillColor
outline=outlineColor
矢量字体支持 TrueType Font support
import ImageFont
ttFont = ImageFont.truetype (“arial.ttf”, 16)
drawable.text ((10, 10), “Hello”, fill=(255,0,0), font=ttFont)
例子:Draw a Grey Cross Over an Image

import Image, ImageDraw im = Image.open("lena.pgm") # Creates an object that can be used to draw in the given image.
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(im) # draw.line(xy, options) => Draws a line between the coordinates in the xy list.
# The coordinate list can be any sequence object containing either 2-tuples [ (x, y), ... ] # or numeric values [ x, y, ... ]. # The fill option gives the color to use for the line.
draw.line((0, 0) + im.size, fill=128) draw.line((0, im.size[1], im.size[0], 0), fill=128) del draw # write to stdout
im.save(sys.stdout, "PNG")

The ImageChops module
a number of arithmetical image operations, called channel operations ("chops" 通道操作).
These can be used for various purposes, including special effects 特殊效果, image compositions 图像合成, algorithmic painting 算法绘画, and more.
At this time, channel operations are only implemented for 8-bit images (e.g. "L" and "RGB").
例子:比较两幅图像
Exact Comparison:
The quickest way to determine if two images have exactly the same contents is to get the difference between the two images, and then calculate the bounding box of the non-zero regions in this image. If the images are identical, all pixels in the difference image are zero, and the bounding box function returns None.
import ImageChops def equal(im1, im2): return ImageChops.difference(im1, im2).getbbox() is None
To get a measure of how similar two images are, you can calculate the root-mean-square (RMS) value of the difference between the images. If the images are exactly identical, this value is zero. The following function uses the difference function, and then calculates the RMS value from the histogram of the resulting image.
RMS Difference:
To get a measure of how similar two images are, you can calculate the root-mean-square (RMS) value of the difference between the images. If the images are exactly identical, this value is zero. The following function uses the difference function, and then calculates the RMS value from the histogram of the resulting image.

# Example: File: imagediff.py
import ImageChops import math, operator def rmsdiff(im1, im2): "Calculate the root-mean-square difference between two images" h = ImageChops.difference(im1, im2).histogram() # calculate rms
return math.sqrt(reduce(operator.add, map(lambda h, i: h*(i**2), h, range(256)) ) / (float(im1.size[0]) * im1.size[1]))

原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/JZ-Ser/p/7230604.html
python图像_Python图像处理库(PIL)相关推荐
- python图像处理模块_Python图像处理库PIL的ImageEnhance模块使用介绍
Python图像处理库PIL的ImageEnhance模块使用介绍 发布时间:2020-08-31 20:08:55 来源:脚本之家 阅读:66 ImageEnhance模块提供了一些用于图像增强的类 ...
- python标准库的图像处理模块_Python图像处理库PIL的ImageFont模块使用介绍
ImageFont模块定义了相同名称的类,即ImageFont类.这个类的实例存储bitmap字体,用于ImageDraw类的text()方法. PIL使用自己的字体文件格式存储bitmap字体.用户 ...
- python图像数据是几维数据_Python图像处理库PIL的ImagePath模块被用于存储和操作二维向量数据...
ImagePath模块被用于存储和操作二维向量数据.Path对象会被传递到ImageDraw模块中. 一.ImagePath模块的函数 1. Path 定义:ImagePath.Path(coordi ...
- python pil是什么_python图像处理库PIL的基本概念介绍
PIL中所涉及的基本概念有如下几个:通道(bands).模式(mode).尺寸(size).坐标系统(coordinate system).调色板(palette).信息(info)和滤波器(filt ...
- python fft库有哪些_Python图像处理库PIL中快速傅里叶变换FFT的实现(一)
离散傅里叶变换(discrete Fouriertransform)傅里叶分析方法是信号分析的最基本方法,傅里叶变换是傅里叶分析的核心,通过它把信号从时间域变换到频率域,进而研究信号的频谱结构和变化规 ...
- python图像分割_Python图像处理库(2)
1.4 SciPy SciPy(http://scipy.org/) 是建立在 NumPy 基础上,用于数值运算的开源工具包.SciPy 提供很多高效的操作,可以实现数值积分.优化.统计.信号处理,以 ...
- python的图像处理库是啥_Python 图像处理库 Pillow 入门
来源:Belial_2010 blog.csdn.net/kezunhai/article/details/46446153 Pillow是Python里的图像处理库(PIL:Python Image ...
- python基础教程:Python图像处理库PIL中图像格式转换的实现
这篇文章主要介绍了Python图像处理库PIL中图像格式转换的实现,文中通过示例代码介绍的非常详细,对大家的学习或者工作具有一定的参考学习价值,需要的朋友们下面随着小编来一起学习学习吧 在数字图像处理 ...
- Python图像处理库PIL中图像格式转换(一)
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/icamera0/article/details/50843172 在数字图像处理中,针对不同的图像格式有其特定的处理算法.所以,在做图像处理之前,我 ...
最新文章
- [JAVA]寻找满足和的最短子序列(Minimum Size Subarray Sum)
- First、FirstOrDefault、Single、SingleOrDefault 的区别
- Intel Media SDK H264 encoder GOP setting
- Eclipse中看不到jsp的页面效果
- windows进程管理器_任务管理器就能搞定9成的电脑问题?方法在这里!
- 晶体封装越小esr越大_晶振
- linux 环境下git的安装与配置
- htm5l,第一个script代码练习
- pop和push等使用方法,every和some、join
- Centos 使用防火墙 Firewalld 进行流量转发
- python3-关于GitHub的最基本操作
- 20190404 Informatic 学习一
- cnpm : 无法加载文件 C:\Users\AppData\Roaming\npm\cnpm.ps1,因为在此系统上禁止运行脚本。的解决方案之一
- 一个在线免费短网址生成API
- welsh-powell
- 软件工程学习(十)常见的软件架构
- 数据结构考研(转载请标明出处,学习辛苦整理)
- java写入文件怎么换行,经验分享
- 解决.Net Core 使用 System.Drawing.Common 在CentOS下报错'Gdip'
- 计算机应届生就业,应届生计算机专业发展方向以及计算机专业就业前景
热门文章
- 如何在Windows 7 Media Center中跳过广告
- 编译卡爆的Android Studio 3.1.1
- python commands模块_python之commands和subprocess入门介绍(可执行shell命令的模块)
- webstorm报错:TS2307: Cannot find module ‘./App.vue‘ or its corresponding type declarations
- 使用SpringBoot获取bean时出错:No qualifying....
- 编译原理SNL语言编译器实验报告
- 华为乾坤王辉:新一代网络安全融合体系,筑牢企业数字化转型基石丨2023 INSEC WORLD
- python写四则运算器_python 简易四则运算计算器
- python:实现ohms law欧姆定律(附完整源码)
- Windows编程之使用GetAsyncKeyState()函数为什么要( 0x8000)?
