递归神经网络的非零初始状态
递归神经网络的非零初始状态
2016年11月20日星期日
原文
初始化RNN状态的默认方法是使用零状态。这通常很有效,特别是对于序列到序列的任务,如语言建模,其中受初始状态影响很大的输出比例很小。然而,在某些情况下,
(1)训练初始状态作为模型参数,
(2)使用嘈杂的初始状态,或
(3)两者都是有意义的。这篇文章简要介绍了训练有素和嘈杂的初始状态背后的基本原理,并介绍了Tensorflow实施的简介。
训练初始状态
如果训练数据中有足够的序列或状态重置(例如,如果我们正在进行序列分类,则通常就是这种情况),将初始状态训练为变量可能是有意义的。这样,模型可以学习一个好的默认状态。但是,如果我们只有少数状态复位,那么将初始状态训练为变量可能会导致每个序列的开始过度拟合。为了看到这一点,考虑使用n步截断反向传播,只有每个序列的前n个步骤将有助于初始状态的梯度,因此即使我们的单个训练序列有一百万步,其中只有三个将用于训练初始状态。
我没有看到有人评价这种技术(编辑11/22/16:虽然它似乎是常识),所以我对实证结果没有很好的引用。相反,请参阅这篇文章中的实验结果。
使用嘈杂的初始状态
使用零值初始状态也可能导致过度拟合,但方式不同。通常,序列到序列模型的早期步骤(即,状态重置后的那些)的损失将大于后续步骤中的损失,因为历史较少。因此,他们在学习期间对梯度的贡献将相对较高。但是如果所有状态复位都与零状态相关联,那么模型可以(并且将会)学习如何精确地补偿这一点。随着状态重置与总观察的比率增加,模型参数将越来越多地调整到该零状态,这可能影响后续时间步骤的性能。
一个简单的解决方案是使初始状态有噪声。这是Zimmerman等人提出的方法。(2012),通过使初始状态噪声的大小根据反向传播误差而改变,甚至更进一步。这篇文章只会让初始状态嘈杂的第一步。
Tensorflow实现
在某些情况下,例如,如在我关于可变长度序列的帖子中,创建可变或有噪声的初始状态以匹配单元状态是直截了当的。但是,我们经常想要切换RNN单元格或构建具有嵌套状态的复杂单元格。我写这篇文章的动机是提供一种方法,如zero_stateTensorflow的基本RNNCell类的方法,它自动构建一个变量或嘈杂的初始状态。
实施模式
我们将在zero_stateTensorflow的基本RNNCell类的方法之后对实现进行建模,如下所示,稍作修改,使其成为顶级函数。您可以在此处查看原始zero_state方法。
import numpy as np, tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.python.util import nest
_state_size_with_prefix = tf.nn.rnn_cell._state_size_with_prefixdef zero_state(cell, batch_size, dtype):"""Return zero-filled state tensor(s).Args:cell: RNNCell.batch_size: int, float, or unit Tensor representing the batch size.dtype: the data type to use for the state.Returns:If `state_size` is an int or TensorShape, then the return value is a`N-D` tensor of shape `[batch_size x state_size]` filled with zeros.If `state_size` is a nested list or tuple, then the return value isa nested list or tuple (of the same structure) of `2-D` tensors withthe shapes `[batch_size x s]` for each s in `state_size`."""state_size = cell.state_sizeif nest.is_sequence(state_size):state_size_flat = nest.flatten(state_size)zeros_flat = [tf.zeros(tf.pack(_state_size_with_prefix(s, prefix=[batch_size])),dtype=dtype)for s in state_size_flat]for s, z in zip(state_size_flat, zeros_flat):z.set_shape(_state_size_with_prefix(s, prefix=[None]))zeros = nest.pack_sequence_as(structure=state_size,flat_sequence=zeros_flat)else:zeros_size = _state_size_with_prefix(state_size, prefix=[batch_size])zeros = tf.zeros(tf.pack(zeros_size), dtype=dtype)zeros.set_shape(_state_size_with_prefix(state_size, prefix=[None]))return zeros履行
我们不是zero_state直接用变量(或带噪声)重写方法来初始化状态,而是抽象出tf.zeros函数,使方法更灵活。我们的抽象函数get_initial_cell_state采用了一个额外的initializer参数,它取代了tf.zeros并决定了状态的初始化方式。这将是一个简单的修改,但是我们需要注意如何创建变量状态(例如,我们不希望批处理中的每个样本使用不同的变量),这会将一些复杂性推入到initializer功能。
def get_initial_cell_state(cell, initializer, batch_size, dtype):"""Return state tensor(s), initialized with initializer.Args:cell: RNNCell.batch_size: int, float, or unit Tensor representing the batch size.initializer: function with two arguments, shape and dtype, thatdetermines how the state is initialized.dtype: the data type to use for the state.Returns:If `state_size` is an int or TensorShape, then the return value is a`N-D` tensor of shape `[batch_size x state_size]` initializedaccording to the initializer.If `state_size` is a nested list or tuple, then the return value isa nested list or tuple (of the same structure) of `2-D` tensors withthe shapes `[batch_size x s]` for each s in `state_size`."""state_size = cell.state_sizeif nest.is_sequence(state_size):state_size_flat = nest.flatten(state_size)init_state_flat = [initializer(_state_size_with_prefix(s), batch_size, dtype, i)for i, s in enumerate(state_size_flat)]init_state = nest.pack_sequence_as(structure=state_size,flat_sequence=init_state_flat)else:init_state_size = _state_size_with_prefix(state_size)init_state = initializer(init_state_size, batch_size, dtype, None)return init_stateinitializer必须是一个带有四个参数的函数:shape和dtype,一个la tf.zeros,另外batch_size还有index,它们被引入以便与变量一起使用。我们可以zero_state使用以下initializer函数实现与原始方法相同的行为:
def zero_state_initializer(shape, batch_size, dtype, index):z = tf.zeros(tf.pack(_state_size_with_prefix(shape, [batch_size])), dtype)z.set_shape(_state_size_with_prefix(shape, prefix=[None]))return z然后调用get_initial_cell_state(cell, zero_state_initializer, batch_size, tf.float32)与调用相同zero_state(cell, batch_size, tf.float32)。
鉴于这种抽象,我们添加了对变量初始化器的支持,如下所示:
def make_variable_state_initializer(**kwargs):def variable_state_initializer(shape, batch_size, dtype, index):args = kwargs.copy()if args.get('name'):args['name'] = args['name'] + '_' + str(index)else:args['name'] = 'init_state_' + str(index)args['shape'] = shapeargs['dtype'] = dtypevar = tf.get_variable(**args)var = tf.expand_dims(var, 0)var = tf.tile(var, tf.pack([batch_size] + [1] * len(shape)))var.set_shape(_state_size_with_prefix(shape, prefix=[None]))return varreturn variable_state_initializer我们现在可以通过调用获得变量初始状态get_initial_cell_state(cell, make_variable_initializer(), batch_size, tf.float32)。
最后,我们可以为零或可变状态的初始化器添加一个嘈杂的包装器,如下所示:
def make_gaussian_state_initializer(initializer, deterministic_tensor=None, stddev=0.3):def gaussian_state_initializer(shape, batch_size, dtype, index):init_state = initializer(shape, batch_size, dtype, index)if deterministic_tensor is not None:return tf.cond(deterministic_tensor,lambda: init_state,lambda: init_state + tf.random_normal(tf.shape(init_state), stddev=stddev))else:return init_state + tf.random_normal(tf.shape(init_state), stddev=stddev)return gaussian_state_initializer这个包装器将高斯噪声添加到底层的initial_state。例如,要创建初始化函数,初始化状态的平均值为零,标准差为0.1,我们调用make_gaussian_state_initializer(zero_state_initializer, stddev=0.01)。deterministic_tensor是一个可选的布尔张量,可用于在测试时禁用添加的噪声(推荐)。
关于截断的PTB数据集的实验
现在让我们在“截断的”PTB语言建模任务上测试我们的初始化器。这将与常规PTB数据集相同,除了我们将修改通常的训练例程以便不向前传播最终状态(即,它将截断状态传播)。通过在每个训练步骤之间重置状态,我们使PTB数据集的行为类似于具有许多状态重置的数据集。
Helper functions
from tensorflow.models.rnn.ptb import reader
from enum import Enum#data from http://www.fit.vutbr.cz/~imikolov/rnnlm/simple-examples.tgz
raw_data = reader.ptb_raw_data('ptb_data')
train_data, val_data, test_data, num_classes = raw_data
batch_size, num_steps = 30, 50def gen_epochs(n, num_steps, batch_size, dataset=train_data):for i in range(n):yield reader.ptb_iterator(dataset, batch_size, num_steps)def reset_graph():if 'sess' in globals() and sess:sess.close()tf.reset_default_graph()def eval_network(sess, g, num_steps = num_steps, batch_size = batch_size):losses = []for X, Y in next(gen_epochs(1, num_steps, batch_size, dataset=val_data+test_data)):feed_dict={g['x']: X, g['y']: Y, g['deterministic']: True}loss_ = sess.run([g['loss']], feed_dict)[0]losses.append(loss_)return np.mean(losses, axis=0)def train_network(sess, g, num_epochs, num_steps = num_steps, batch_size = batch_size):sess.run(tf.initialize_all_variables())losses = []val_losses = []for idx, epoch in enumerate(gen_epochs(num_epochs, num_steps, batch_size)):loss = []for X, Y in epoch:feed_dict={g['x']: X, g['y']: Y}loss_, _ = sess.run([g['loss'], g['train_step']], feed_dict)loss.append(loss_)val_loss = eval_network(sess, g)print("Average perplexity for Epoch", idx,": Training -", np.exp(np.mean(loss)),"Validation -", np.exp(np.mean(val_loss)))losses.append(np.mean(loss, axis=0))val_losses.append(val_loss)return np.array(losses), np.array(val_losses)class StateInitializer(Enum):ZERO_STATE = 1VARIABLE_STATE = 2NOISY_ZERO_STATE = 3NOISY_VARIABLE_STATE = 4Graph
def build_graph(state_initializer,state_size = 200,num_classes = num_classes,batch_size = batch_size,num_steps = num_steps,num_layers = 2):reset_graph()x = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, [batch_size, num_steps], name='input_placeholder')y = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, [batch_size, num_steps], name='labels_placeholder')lr = tf.constant(1.)deterministic = tf.constant(False)embeddings = tf.get_variable('embedding_matrix', [num_classes, state_size])rnn_inputs = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(embeddings, x)cell = tf.nn.rnn_cell.LSTMCell(state_size, state_is_tuple=True)cell = tf.nn.rnn_cell.MultiRNNCell([cell] * num_layers, state_is_tuple=True)if state_initializer == StateInitializer.ZERO_STATE:initializer = zero_state_initializerelif state_initializer == StateInitializer.VARIABLE_STATE:initializer = make_variable_state_initializer()elif state_initializer == StateInitializer.NOISY_ZERO_STATE:initializer = make_gaussian_state_initializer(zero_state_initializer,deterministic)elif state_initializer == StateInitializer.NOISY_VARIABLE_STATE:initializer = make_gaussian_state_initializer(make_variable_state_initializer(),deterministic)init_state = get_initial_cell_state(cell, initializer, batch_size, tf.float32)rnn_outputs, final_state = tf.nn.dynamic_rnn(cell, rnn_inputs, initial_state=init_state)with tf.variable_scope('softmax'):W = tf.get_variable('W', [state_size, num_classes])b = tf.get_variable('b', [num_classes], initializer=tf.constant_initializer(0.0))#reshape rnn_outputs and y so we can get the logits in a single matmulrnn_outputs = tf.reshape(rnn_outputs, [-1, state_size])y_reshaped = tf.reshape(y, [-1])logits = tf.matmul(rnn_outputs, W) + blosses = tf.reshape(tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits, y_reshaped),[batch_size, num_steps])loss_by_timestep = tf.reduce_mean(losses, reduction_indices=0)train_step = tf.train.AdamOptimizer().minimize(loss_by_timestep)return dict(x = x,y = y,lr = lr,deterministic = deterministic,init_state = init_state,final_state = final_state,loss = loss_by_timestep,train_step = train_step)实验
tr_losses, val_losses = [None] * 4, [None] * 4
g = build_graph(state_initializer=StateInitializer.ZERO_STATE)
sess = tf.InteractiveSession()
tr_losses[0], val_losses[0] = train_network(sess, g, num_epochs=20)Average perplexity for Epoch 0 : Training - 674.599 Validation - 483.888
Average perplexity for Epoch 1 : Training - 421.366 Validation - 348.751
Average perplexity for Epoch 2 : Training - 305.943 Validation - 272.674
Average perplexity for Epoch 3 : Training - 241.748 Validation - 235.801
Average perplexity for Epoch 4 : Training - 205.29 Validation - 212.853
Average perplexity for Epoch 5 : Training - 180.5 Validation - 198.029
Average perplexity for Epoch 6 : Training - 160.867 Validation - 186.862
Average perplexity for Epoch 7 : Training - 145.657 Validation - 179.394
Average perplexity for Epoch 8 : Training - 133.973 Validation - 173.399
Average perplexity for Epoch 9 : Training - 124.281 Validation - 169.236
Average perplexity for Epoch 10 : Training - 115.586 Validation - 166.216
Average perplexity for Epoch 11 : Training - 108.34 Validation - 163.99
Average perplexity for Epoch 12 : Training - 101.959 Validation - 162.627
Average perplexity for Epoch 13 : Training - 96.3985 Validation - 162.423
Average perplexity for Epoch 14 : Training - 91.6309 Validation - 163.904
Average perplexity for Epoch 15 : Training - 87.29 Validation - 163.679
Average perplexity for Epoch 16 : Training - 83.2224 Validation - 164.169
Average perplexity for Epoch 17 : Training - 79.5156 Validation - 165.162
Average perplexity for Epoch 18 : Training - 76.1198 Validation - 166.714
Average perplexity for Epoch 19 : Training - 73.1628 Validation - 168.515g = build_graph(state_initializer=StateInitializer.VARIABLE_STATE)
sess = tf.InteractiveSession()
tr_losses[1], val_losses[1] = train_network(sess, g, num_epochs=20)Average perplexity for Epoch 0 : Training - 525.724 Validation - 325.364
Average perplexity for Epoch 1 : Training - 275.811 Validation - 239.312
Average perplexity for Epoch 2 : Training - 210.521 Validation - 204.103
Average perplexity for Epoch 3 : Training - 176.135 Validation - 184.352
Average perplexity for Epoch 4 : Training - 153.307 Validation - 171.528
Average perplexity for Epoch 5 : Training - 136.591 Validation - 162.493
Average perplexity for Epoch 6 : Training - 123.592 Validation - 156.533
Average perplexity for Epoch 7 : Training - 113.033 Validation - 152.028
Average perplexity for Epoch 8 : Training - 104.201 Validation - 149.743
Average perplexity for Epoch 9 : Training - 96.7272 Validation - 148.263
Average perplexity for Epoch 10 : Training - 90.313 Validation - 147.438
Average perplexity for Epoch 11 : Training - 84.7536 Validation - 147.409
Average perplexity for Epoch 12 : Training - 79.8758 Validation - 147.533
Average perplexity for Epoch 13 : Training - 75.5331 Validation - 148.11
Average perplexity for Epoch 14 : Training - 71.5848 Validation - 149.513
Average perplexity for Epoch 15 : Training - 67.9394 Validation - 151.243
Average perplexity for Epoch 16 : Training - 64.6299 Validation - 153.503
Average perplexity for Epoch 17 : Training - 61.6355 Validation - 156.37
Average perplexity for Epoch 18 : Training - 58.9116 Validation - 160.145
Average perplexity for Epoch 19 : Training - 56.4397 Validation - 164.863g = build_graph(state_initializer=StateInitializer.NOISY_ZERO_STATE)
sess = tf.InteractiveSession()
tr_losses[2], val_losses[2] = train_network(sess, g, num_epochs=20)Average perplexity for Epoch 0 : Training - 625.676 Validation - 407.948
Average perplexity for Epoch 1 : Training - 337.045 Validation - 277.074
Average perplexity for Epoch 2 : Training - 245.198 Validation - 230.573
Average perplexity for Epoch 3 : Training - 202.941 Validation - 205.394
Average perplexity for Epoch 4 : Training - 175.752 Validation - 189.294
Average perplexity for Epoch 5 : Training - 156.077 Validation - 178.006
Average perplexity for Epoch 6 : Training - 141.035 Validation - 170.011
Average perplexity for Epoch 7 : Training - 128.985 Validation - 164.033
Average perplexity for Epoch 8 : Training - 118.946 Validation - 160.09
Average perplexity for Epoch 9 : Training - 110.475 Validation - 157.405
Average perplexity for Epoch 10 : Training - 103.191 Validation - 155.624
Average perplexity for Epoch 11 : Training - 96.9187 Validation - 154.584
Average perplexity for Epoch 12 : Training - 91.4146 Validation - 154.25
Average perplexity for Epoch 13 : Training - 86.494 Validation - 154.48
Average perplexity for Epoch 14 : Training - 82.1429 Validation - 155.172
Average perplexity for Epoch 15 : Training - 78.1957 Validation - 156.681
Average perplexity for Epoch 16 : Training - 74.6005 Validation - 158.523
Average perplexity for Epoch 17 : Training - 71.3612 Validation - 160.869
Average perplexity for Epoch 18 : Training - 68.3056 Validation - 163.278
Average perplexity for Epoch 19 : Training - 65.4805 Validation - 165.645g = build_graph(state_initializer=StateInitializer.NOISY_VARIABLE_STATE)
sess = tf.InteractiveSession()
tr_losses[3], val_losses[3] = train_network(sess, g, num_epochs=20)Average perplexity for Epoch 0 : Training - 517.27 Validation - 331.341
Average perplexity for Epoch 1 : Training - 278.846 Validation - 239.6
Average perplexity for Epoch 2 : Training - 210.333 Validation - 203.027
Average perplexity for Epoch 3 : Training - 174.959 Validation - 182.456
Average perplexity for Epoch 4 : Training - 151.81 Validation - 169.388
Average perplexity for Epoch 5 : Training - 135.121 Validation - 160.613
Average perplexity for Epoch 6 : Training - 122.301 Validation - 154.474
Average perplexity for Epoch 7 : Training - 111.991 Validation - 150.337
Average perplexity for Epoch 8 : Training - 103.425 Validation - 147.664
Average perplexity for Epoch 9 : Training - 96.1806 Validation - 145.957
Average perplexity for Epoch 10 : Training - 89.8921 Validation - 145.308
Average perplexity for Epoch 11 : Training - 84.3145 Validation - 145.255
Average perplexity for Epoch 12 : Training - 79.3745 Validation - 146.052
Average perplexity for Epoch 13 : Training - 74.96 Validation - 147.01
Average perplexity for Epoch 14 : Training - 71.0005 Validation - 148.22
Average perplexity for Epoch 15 : Training - 67.3658 Validation - 150.713
Average perplexity for Epoch 16 : Training - 64.0655 Validation - 153.78
Average perplexity for Epoch 17 : Training - 61.0874 Validation - 157.101
Average perplexity for Epoch 18 : Training - 58.3892 Validation - 160.376
Average perplexity for Epoch 19 : Training - 55.9478 Validation - 164.157import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
import seaborn as sns
sns.set(color_codes=True)def best_epoch(val_losses):return np.argmin(np.mean(val_losses, axis=1))labels = ['Zero', 'Variable', 'Noisy', 'Noisy Variable']def plot_losses(losses, title, y_range):global val_lossesfig, ax = plt.subplots()for i in range(len(losses)):data = np.exp(losses[i][best_epoch(val_losses[i])])ax.plot(range(0,num_steps),data,label=labels[i])ax.set_xlabel('Step number')ax.set_ylabel('Average loss')ax.set_ylim(y_range)ax.set_title(title)ax.legend(loc=1)plt.show()plot_losses(tr_losses, 'Best epoch training perplexities', [70, 110])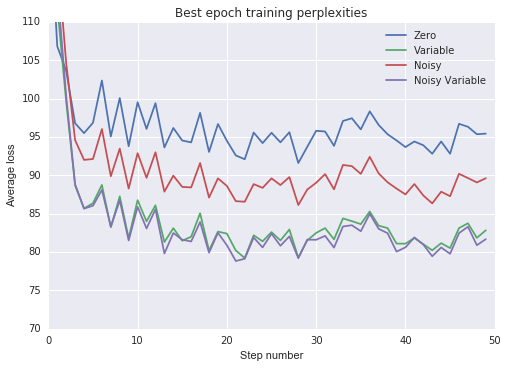
plot_losses(val_losses, 'Best epoch validation perplexities', [120, 200])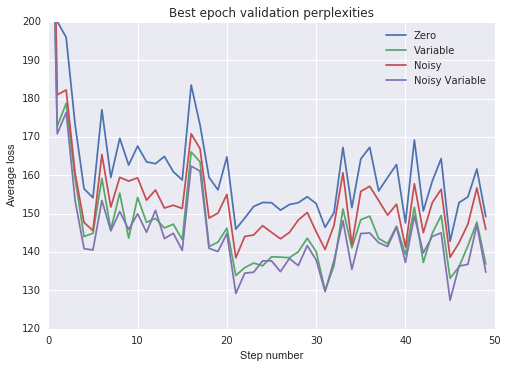
实验结果
从上述实验中我们得出以下观察结果:
- 所有非零状态初始化加速了训练并改进了泛化。
- 将初始状态训练为变量比使用噪声零均值初始状态更有效。
- 将噪声添加到可变初始状态仅提供边际效益。
最后,我会注意到,“截断”PTB数据集会产生比未截断数据集时获得的结果更差的结果,即使我们使用噪声或可变状态初始化。我们可以通过将上述结果与Zaremba等人的“非正规化LSTM”进行比较来看出这一点。(2015),它具有非常相似的架构,但没有截断数据集中的序列。我希望截断通常具有这种效果,因此这些非零状态初始化仅对具有许多自然发生状态重置的数据集非常有用。
递归神经网络的非零初始状态相关推荐
- 一种递归式的非零自然数全分解方法
一种递归式的非零自然数全分解方法 在开始讲之前,首先介绍一下这个方法针对的问题背景:一个非零自然数(1,2,3,--)既不重复也不遗漏地任意分解为非零自然数(如:3=1+1+1=1+2),我在本篇 ...
- 快排递归非递归python_Python递归神经网络终极指南
快排递归非递归python Recurrent neural networks are deep learning models that are typically used to solve ti ...
- 零基础入门深度学习(7) - 递归神经网络
无论即将到来的是大数据时代还是人工智能时代,亦或是传统行业使用人工智能在云上处理大数据的时代,作为一个有理想有追求的程序员,不懂深度学习(Deep Learning)这个超热的技术,会不会感觉马上就o ...
- 系统学习深度学习(五) --递归神经网络原理,实现及应用
递归神经网络(RNN),是两种人工神经网络的总称,一种是时间递归神经网络(recurrent neural network),另一种是结构递归神经网络(recursive neur ...
- lecture7-序列模型及递归神经网络RNN
Hinton 第七课 .这里先说下RNN有recurrent neural network 和 recursive neural network两种,是不一样的,前者指的是一种人工神经网络,后者指的是 ...
- 基于递归神经网络的人脸识别探究
摘要 本文首先简介了人工神经网络的发展史,继而介绍了递归神经网络的理论以及百度在基于递归神经网络的应用研究,最后探讨了递归神经网络在人脸识别中的应用. 1. 人工神经网络发展史[1][2] 人工 ...
- 使用卷积和递归神经网络通过序列和本体表示改进circRNA-疾病关联预测
摘要: 新的研究表明,环状RNA(CircRNA)广泛参与人类疾病的进展.由于其特殊的稳定结构,CircRNA是很有前途的疾病诊断和预后生物标志物.然而,circRNA-疾病关联的实验验证成本高昂,且 ...
- 循环神经网络 递归神经网络_如何用递归神经网络预测空气污染
循环神经网络 递归神经网络 After the citizen science project of Curieuze Neuzen, I wanted to learn more about air ...
- DeepMind提图像生成的递归神经网络DRAW,158行Python代码复现
作者 | Samuel Noriega 译者 | Freesia 编辑 | 夕颜 出品 | AI科技大本营(ID: rgznai100) [导读]最近,谷歌 DeepMInd 发表论文( DRAW: ...
- 158行Python代码复现:DeepMind提图像生成的递归神经网络DRAW
授权自AI科技大本营(ID:rgznai100) 本文约5200字,建议阅读10+分钟. 本文作者基于代码实现系统的思路,详细阐述了 DRAW 的概念.架构和优势等. [ 导读 ]最近,谷歌 Deep ...
最新文章
- php文件上传代码_PHP实现文件分片上传的实例代码
- 后置处理器----JSON提取器
- Open 5分钟:恺英收集闵懿
- 理解单例模式、单例类
- 搭建DNS主、从服务实验
- 示波器纹波测试的时间设置_500W电源横评:输出纹波3款电源超标
- 19.Linux系统管理
- 2007 Microsoft Office 加载项:Microsoft Save as PDF 或 XPS
- 从零开始编译LEDE固件 默认中文material主题_php_sir_新浪博客
- 计算机图形学结课论文,计算机图形学的结课论文计算机图形学课程期末论文
- 计算机管理磁盘分区,一分钟搞定电脑磁盘分区,再也不求人!
- 35岁以后的大龄程序员,正处于怎样一种状态?
- 如何在Python中使用Rest API
- 四咪唑基四苯乙烯,四苯基吡嗪(tetraphenylpyrazine,TPP)
- 地理信息系统(Geographic Information System或 Geo-Information system,GIS)
- 正则表达式---省、自治区、直辖市
- Mac OS + Mac PE + Win PE 三合一 U盘制作教程
- 关于买房的后的人生感悟
- php 股票动态图,股票动态图,看懂了秒变高手!
- idea搭建bpm环境
热门文章
- php 抽象类 接口 区别,php中接口、抽象类以及接口和抽象类区别详解
- mysql 吞吐量测试工具_MySQL基准测试工具--sysbench
- 赛题解读 | 如何基于 Flink + AI 解决疫情防控难题?
- 外包征集令:一个Android TV酒店项目
- linux 终端 收取邮件,linux mail 命令 (收发邮件)
- 扫地机器人 杂牌_国内扫地机器人哪个牌子好?
- unity创建一个简单对象的开销_SpringBoot第一篇:创建一个简单的SpringBoot
- many to many mysql_mysql “Too many connections” 解决办法
- coreldraw x4忽略视图样式补丁_80%的人都忽略了PPT画布之外的用法,但这6点真的很实用...
- go语言阶段综合练习--家庭收支软件的示例--过程版本
