Android Bundle详解
1 Bundle介绍
Bundle主要用于传递数据;它保存的数据,是以key-value(键值对)的形式存在的。
我们经常使用Bundle在Activity之间传递数据,传递的数据可以是boolean、byte、int、long、float、double、string等基本类型或它们对应的数组,也可以是对象或对象数组。当Bundle传递的是对象或对象数组时,必须实现Serializable 或Parcelable接口。下面分别介绍Activity之间如何传递基本类型、传递对象。
2传递基本类型
Bundle提供了各种常用类型的putXxx()/getXxx()方法,用于读写基本类型的数据。Bundle操作基本数据类型的API表格如下所示:
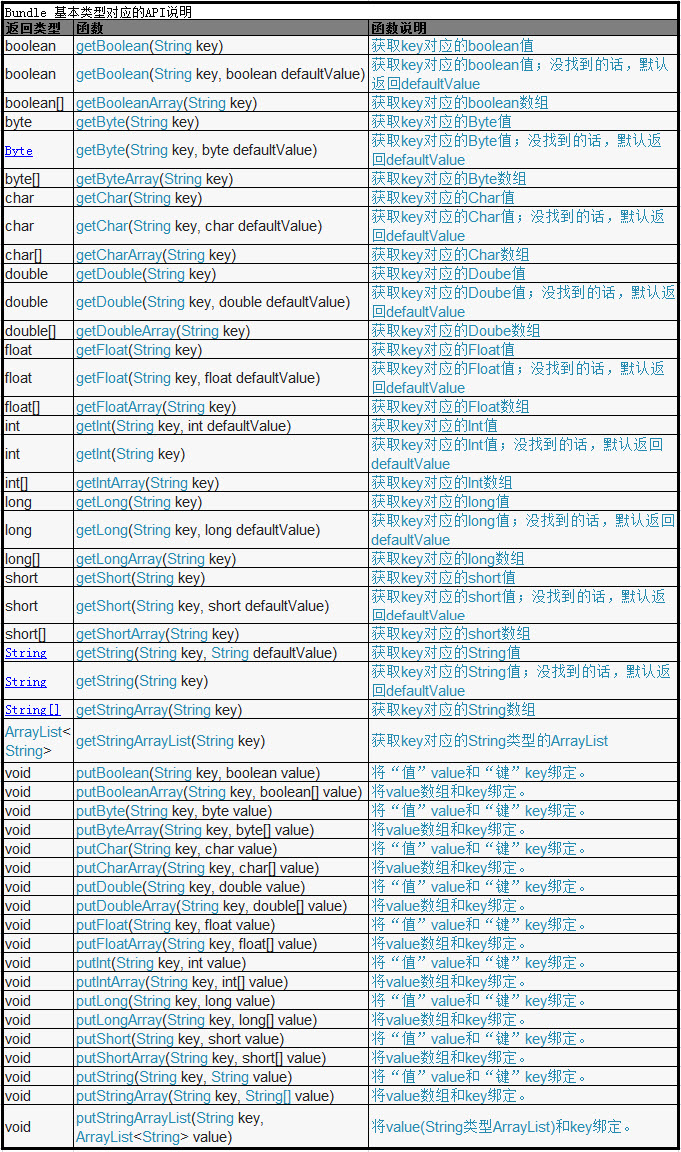
写数据的方法如下:
// "com.test" is the package name of the destination class
// "com.test.Activity02" is the full class path of the destination class
Intent intent = new Intent().setClassName("com.bundletest", "com.bundletest.Bundle02");Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
bundle.putString("name", "skywang");
bundle.putInt("height", 175);
intent.putExtras(bundle);startActivity(intent);// end current class
finish();对应的读数据的方法如下:
Bundle bundle = this.getIntent().getExtras(); String name = bundle.getString("name");
int height = bundle.getInt("height");3传递Parcelable类型的对象
3.1 Parcelable说明
Parcelable是Android自定义的一个接口,它包括了将数据写入Parcel和从Parcel中读出的API。一个实体(用类来表示),如果需要封装到bundle消息中去,可以通过实现Parcelable接口来实现。
Parcelable和Serializable的API如下表:
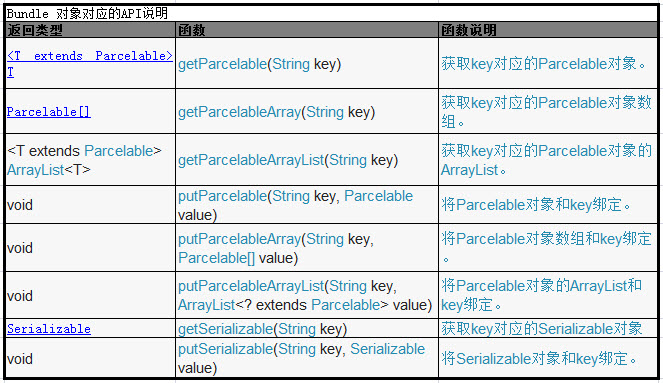
3.2 Parcelable接口说明
public interface Parcelable {//内容描述接口,基本不用管public int describeContents();//写入接口函数,打包public void writeToParcel(Parcel dest, int flags);//读取接口,目的是要从Parcel中构造一个实现了Parcelable的类的实例处理。因为实现类在这里还是不可知的,所以需要用到模板的方式,继承类名通过模板参数传入。//为了能够实现模板参数的传入,这里定义Creator嵌入接口,内含两个接口函数分别返回单个和多个继承类实例。public interface Creator<T> {public T createFromParcel(Parcel source);public T[] newArray(int size);}
}
3.3 Parcelable接口的实现方法
从parcelable接口定义中,我们可以看到,实现parcelable接口,需要我们实现下面几个方法:
(01)describeContents方法。内容接口描述,默认返回0就可以;
(02)writeToParcel 方法。该方法将类的数据写入外部提供的Parcel中.即打包需要传递的数据到Parcel容器保存,以便从parcel容器获取数据,该方法声明如下:
writeToParcel(Parcel dest, int flags) 具体参数含义见doc文档
(3.)静态的Parcelable.Creator接口,本接口有两个方法:
createFromParcel(Parcelin) 从Parcel容器中读取传递数据值,封装成Parcelable对象返回逻辑层。
newArray(int size) 创建一个类型为T,长度为size的数组,仅一句话(returnnew T[size])即可。方法是供外部类反序列化本类数组使用。
4传递Serializable类型的对象
4.1 Serializable说明
Serializable是一个对象序列化的接口。一个类只有实现了Serializable接口,它的对象才是可序列化的。因此如果要序列化某些类的对象,这些类就必须实现Serializable接口。而实际上,Serializable是一个空接口,没有什么具体内容,它的目的只是简单的标识一个类的对象可以被序列化。
4.2 Serializable接口的实现方法
很简单,只要implements Serializable接口就可以了
5 demo演示程序
下面是对实现上述三种数据传递方式的BundleTest(demo程序)进行简要介绍
5.1 demo概要
BundleTest共包含了4个java文件和2个layout文件(main.xml和main2.xml)
Bundle01.java —— 默认的主Activity窗口。
Bundle02.java —— 主Activity用于跳转的目的窗口。
Book.java —— 实现Parcelable接口的类
Person.java —— 实现Serializable接口的类
main.xml —— Bundle01.java的layout文件
main2.xml —— Bundle02.java的layout文件
工程文件结构如下所示:
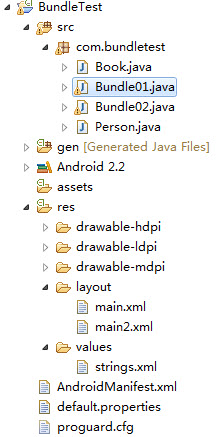
5.2代码
AndroidManifest.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"package="com.bundletest"android:versionCode="1"android:versionName="1.0"><application android:icon="@drawable/icon" android:label="@string/app_name"><activity android:name=".Bundle01"android:label="@string/app_name"><intent-filter><action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /><category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" /></intent-filter></activity><activity android:name=".Bundle02"> </activity></application><uses-sdk android:minSdkVersion="11" />
</manifest>
main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"android:orientation="vertical"android:layout_width="fill_parent"android:layout_height="fill_parent"><TextView android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="@string/app_01"/><Button android:id="@+id/btnBasic" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="@string/text_basic"/><Button android:id="@+id/btnPar" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="@string/text_par"/><Button android:id="@+id/btnSer" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="@string/text_ser"/></LinearLayout>
main2.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"android:orientation="vertical"android:layout_width="fill_parent"android:layout_height="fill_parent"><TextView android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="@string/app_02"/><Button android:id="@+id/btnBack" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="@string/text_jump_back"/></LinearLayout>
strings.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources><string name="hello">Hello MyBundleTest!</string><string name="app_name">MyBundleTest</string><string name="app_01">Bundle_01</string><string name="app_02">Bundle_02</string><string name="text_basic">Bundle Basic Data</string><string name="text_par">Bundle Parcelable Data</string><string name="text_ser">Bundle Seriable Data</string><string name="text_jump_back">Jump Back to Bundler01</string>
</resources>
Bundle01.java
package com.bundletest;import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.util.Log;public class Bundle01 extends Activity implements View.OnClickListener{private static final String TAG = "skywang-->Bundle01";private Button mBtnBasic = null;private Button mBtnPar = null;private Button mBtnSer = null;@Overridepublic void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);setContentView(R.layout.main);mBtnBasic = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnBasic);mBtnBasic.setOnClickListener(this);mBtnPar = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnPar);mBtnPar.setOnClickListener(this);mBtnSer = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnSer);mBtnSer.setOnClickListener(this);}@Overridepublic void onClick(View view) {switch (view.getId()) {case R.id.btnBasic:sendBasicDataThroughBundle();break;case R.id.btnPar:sendParcelableDataThroughBundle();break;case R.id.btnSer:sendSeriableDataThroughBundle();break;default:break;}}// sent basic data, such as int, strin, etc... through bundleprivate void sendBasicDataThroughBundle(){ // "com.test" is the package name of the destination class// "com.test.Activity02" is the full class path of the destination classIntent intent = new Intent().setClassName("com.bundletest", "com.bundletest.Bundle02");Bundle bundle = new Bundle();bundle.putString("name", "skywang");bundle.putInt("height", 175);intent.putExtras(bundle);startActivity(intent);// end current classfinish();}// sent object through Pacelableprivate void sendParcelableDataThroughBundle(){ Intent intent = new Intent().setClassName("com.bundletest", "com.bundletest.Bundle02");Book mBook = new Book();mBook.setBookName("Android");mBook.setAuthor("skywang");mBook.setPublishTime(2013);Bundle mBundle = new Bundle();mBundle.putParcelable("ParcelableValue", mBook);intent.putExtras(mBundle);startActivity(intent);finish();}// sent object through seriableprivate void sendSeriableDataThroughBundle(){ Intent intent = new Intent().setClassName("com.bundletest", "com.bundletest.Bundle02");Person mPerson = new Person();mPerson.setName("skywang");mPerson.setAge(24);Bundle mBundle = new Bundle();mBundle.putSerializable("SeriableValue",mPerson);intent.putExtras(mBundle);startActivity(intent);finish();}}
Bundle02.java
package com.bundletest;import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.util.Log;public class Bundle02 extends Activity implements View.OnClickListener {private static final String TAG = "skywang-->Bundle02";private Button mBtnBack = null;@Overridepublic void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);setContentView(R.layout.main2);mBtnBack = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnBack);mBtnBack.setOnClickListener(this);receiveBasicData();receiveParcelableData();receiveSeriableData();}private void receiveBasicData() {Bundle bundle = this.getIntent().getExtras(); String name = bundle.getString("name"); int height = bundle.getInt("height");if (name != null && height != 0)Log.d(TAG, "receice basic data -- " +"name="+name+", height="+height);}private void receiveParcelableData() {Book mBook = (Book)getIntent().getParcelableExtra("ParcelableValue");if (mBook != null)Log.d(TAG, "receice parcel data -- " +"Book name is: " + mBook.getBookName()+", "+"Author is: " + mBook.getAuthor() + ", "+"PublishTime is: " + mBook.getPublishTime());}private void receiveSeriableData() {Person mPerson = (Person)getIntent().getSerializableExtra("SeriableValue"); if (mPerson != null)Log.d(TAG, "receice serial data -- " +"The name is:" + mPerson.getName() + ", "+"age is:" + mPerson.getAge()); }@Overridepublic void onClick(View view) {switch (view.getId()) {case R.id.btnBack:{// "com.test" is the package name of the destination class// "com.test.Activity01" is the full class path of the destination classIntent intent = new Intent().setClassName("com.bundletest", "com.bundletest.Bundle01");startActivity(intent);// end current classfinish();}break;default:break;}}}
Book.java
package com.bundletest;import android.os.Parcel;
import android.os.Parcelable; public class Book implements Parcelable { private String bookName; private String author; private int publishTime; public String getBookName() { return bookName; } public void setBookName(String bookName) { this.bookName = bookName; } public String getAuthor() { return author; } public void setAuthor(String author) { this.author = author; } public int getPublishTime() { return publishTime; } public void setPublishTime(int publishTime) { this.publishTime = publishTime; } public static final Parcelable.Creator<Book> CREATOR = new Creator<Book>() { @Overridepublic Book createFromParcel(Parcel source) { Book mBook = new Book(); mBook.bookName = source.readString(); mBook.author = source.readString(); mBook.publishTime = source.readInt(); return mBook; } @Overridepublic Book[] newArray(int size) { return new Book[size]; } }; @Overridepublic int describeContents() { return 0; } @Overridepublic void writeToParcel(Parcel parcel, int flags) { parcel.writeString(bookName); parcel.writeString(author); parcel.writeInt(publishTime); }
}
Person.java
package com.bundletest;import java.io.Serializable; public class Person implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; private String name; private int age; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } }
5.3输出图片
Bundle01.java对应的界面如下:
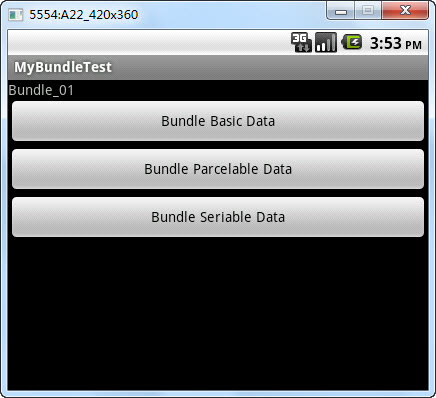
点击“Bundle Basic Data”、“Bundle Parcelable Data”、“Bundle Seriable Data”均跳转到如下界面,但它们对应的logcat信息不同。
点击“Bundle Basic Data”的logcat如下:
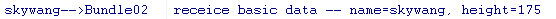
点击“Bundle Parcelable Data”的logcat如下:
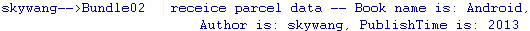
点击“Bundle Seriable Data”的logcat如下:

转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/skywang12345/archive/2013/03/06/3165555.html
Android Bundle详解相关推荐
- 【转】Android菜单详解——理解android中的Menu--不错
原文网址:http://www.cnblogs.com/qingblog/archive/2012/06/08/2541709.html 前言 今天看了pro android 3中menu这一章,对A ...
- Android菜单详解——理解android中的Menu
前言 今天看了pro android 3中menu这一章,对Android的整个menu体系有了进一步的了解,故整理下笔记与大家分享. PS:强烈推荐<Pro Android 3>,是我至 ...
- android WebView详解,常见漏洞详解和安全源码(下)
上篇博客主要分析了 WebView 的详细使用,这篇来分析 WebView 的常见漏洞和使用的坑. 上篇:android WebView详解,常见漏洞详解和安全源码(上) 转载请注明出处:http ...
- android子视图无菜单,Android 菜单详解
Android中菜单分为三种,选项菜单(OptionMenu),上下文菜单(ContextMenu),子菜单(SubMenu) 选项菜单 可以通过两种办法增加选项菜单,一是在menu.xml中添加,该 ...
- Android SharedFlow详解
转载请标明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/zhaoyanjun6/article/details/121911675 本文出自[赵彦军的博客] 文章目录 系列文章 什么是SharedF ...
- android fragment 优势,Android Fragment详解
参考网址:Android Fragment详解 一.什么是Fragment? Fragment:是Android3.0开始新增的概念,意为碎片.Fragment是依赖于Activity的,不能独立存在 ...
- Android Notification 详解——基本操作
Android Notification 详解 版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载. 前几天项目中有用到 Android 通知相关的内容,索性把 Android Notificatio ...
- android rotate 动画,Android RotateAnimation详解
RotateAnimation旋转坐标系为以旋转点为坐标系(0,0)点.x轴为0度,顺时针方向旋转一定的角度. 1.RotateAnimation(fromDegrees, toDegrees) [默 ...
- Android 多线程详解
Android 多线程详解 一.多线程介绍 在学习多线程之前我们首先要了解几个与多线程有关的概念. 进程:进程指正在运行的程序.确切的来说,当一个程序进入内存运行,即变成一个进程,进程是处于运行过程中 ...
最新文章
- 操作系统学习1:操作系统概述
- .Net SqlDbHelper
- JDK源码解析 Comparator 中的策略模式
- python无符号转有符号_Python | 散布符号
- 在ubuntu上安装Oracle Java SDK
- C语言分支循环结构1,c语言——运算符、分支结构、循环结构(示例代码)
- atitit.php 流行框架 前三甲为:Laravel、Phalcon、Symfony2 attilax 总结
- Qt网络编程-简易版UDP单播通信入门Demo(3)
- VR是什么,去哪里学习?
- 华为路由器显示连接到服务器失败怎么办,华为路由器设置好后不能上网怎么办...
- MikTex+texworks插入数学公式示例
- 区分map和fileter
- Filter过滤器导致CSS样式失效
- arm-linux东东之nand之一:nand 初始化
- 缓冲、运放、跟随电路详解及区分
- vue3+ts+ant-table横向表格数据实现对单元格过滤之后的数据进行标红
- 衡阳高铁铁路学校计算机专业,衡阳2021年铁路学校都有哪些专业好
- 贝岭ADC(BL1063/BLAD16J125)使用和配置问题
- AcrelEMS企业能效管理平台
- 茶的文化我宣传|茶叶储存
